
The traffic rules describe how a road user must act on the public road, which includes obligations but also advice on how to drive sensibly and safely. All road users must know and apply the traffic rules.
The public road contains the lane, bicycle path, footpath and roadside and goes all the way to the canal or a property. On public roads we are allowed to drive with all vehicles (if no restrictions are imposed by traffic signs).
The roadway or carriageway is a part of the public road intended for the movement of vehicles. The lane is intended for the traffic of cars, trucks, buses, tractors and motorbikes. If there is no footpath or bicycle path, pedestrians and cyclists also use the roadway.
 A roadway can be split into different lanes.
A roadway can be split into different lanes.
The bike path is part of the public road intended for the traffic of cyclists. If a bike path is available, cyclists must use it. The bike path is not part of the roadway. Cars may not park, stand or drive on the cycle path.
The footpath is the part of the public road intended for pedestrian traffic. Sometimes it is also called a pavement or sidewalk. If a footpath is present, pedestrians must use it.
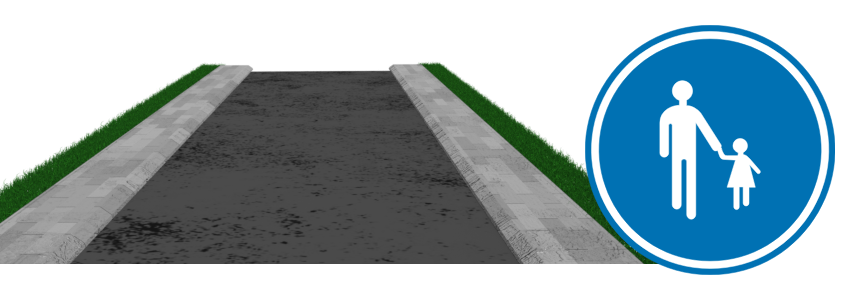 If there is a footpath, then pedestrians must use it.
If there is a footpath, then pedestrians must use it.
A verge is a strip of soil along a road and is often planted with grass, plants or trees. Road signs are often placed in the roadside. If the road is too narrow to cross another vehicle, you can move on the roadside.
 The verge is part of the public road.
The verge is part of the public road.
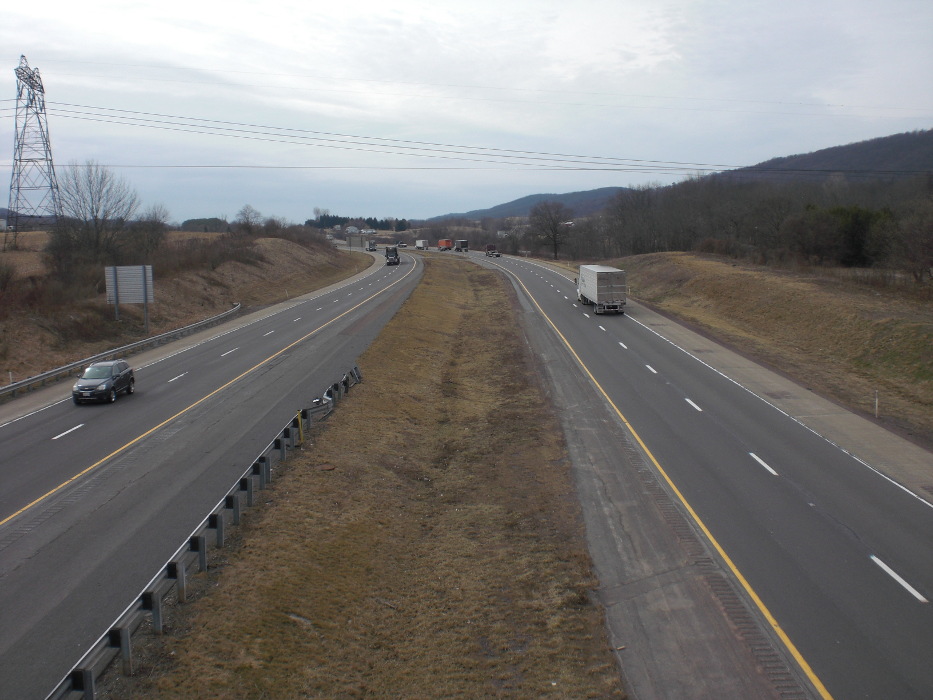 Some roads have a median strip to separate the direction of travel.
Some roads have a median strip to separate the direction of travel.
A public space is a place where we will only come if we have to be there for something. The traffic regulations only apply to public roads, but it is usually also applied to a (non-) public area.
A private property is a place where we can only come if we have permission to do so. For example a parking lot of a company, a private road or a driveway of a garage.
 Petrol station.
Petrol station.
 Parking of a store.
Parking of a store.
 Private parking.
Private parking.
 Parking of a company.
Parking of a company.
Roadmarks are used on paved roadways to provide guidance and information to drivers and pedestrians. Uniformity of the markings is an important factor in minimizing confusion and uncertainty about their meaning, and efforts exist to standardize such markings across borders. However, countries and areas categorize and specify road surface markings in different ways.


A crossing is a location on the road that is intended to cross and which is marked as such. They are for pedestrians and cyclists.
 Warning for a crossing for pedestrians.
Warning for a crossing for pedestrians.
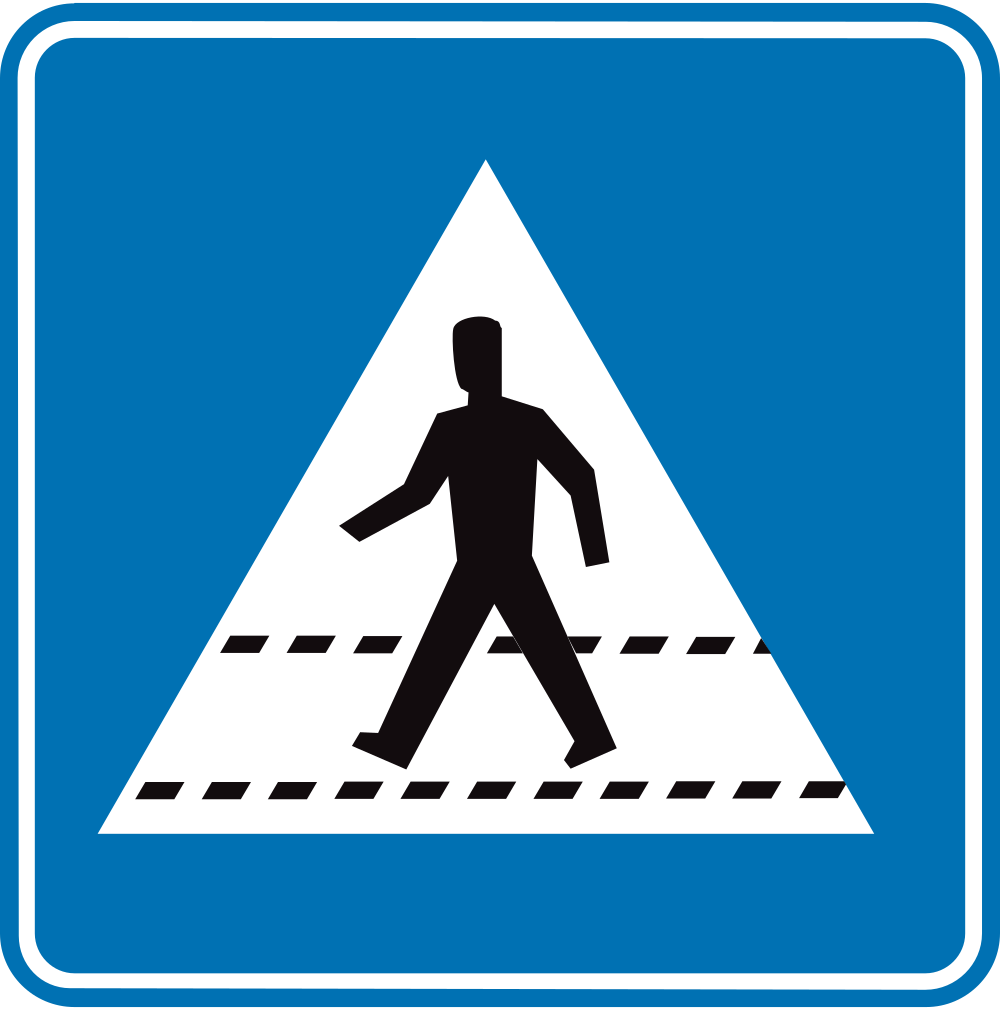 Crossing for pedestrians.
Crossing for pedestrians.
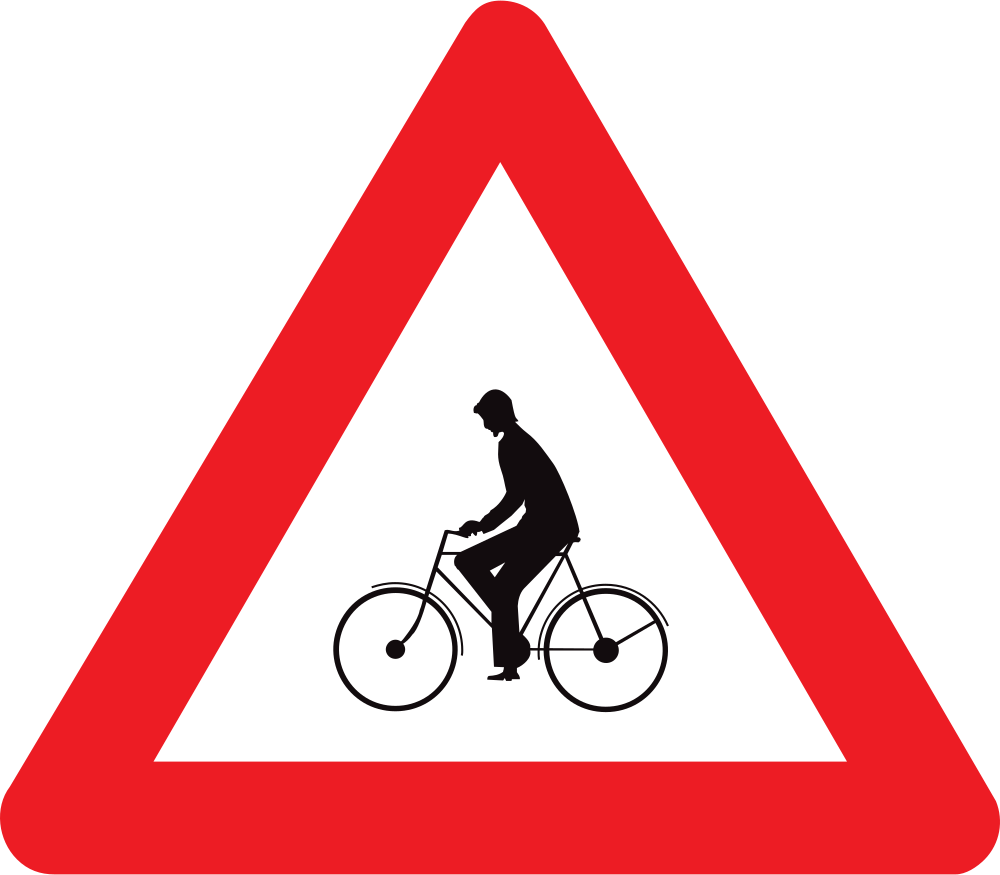 Warning for cyclists.
Warning for cyclists.
A low-emission zone is a selective admission policy for motor vehicles is used in relation to the environmental nuisance caused by these vehicles because of the quality of life, in particular the environmental and health problems caused by poor air quality.
 Begin of a low-emission zone.
Begin of a low-emission zone.
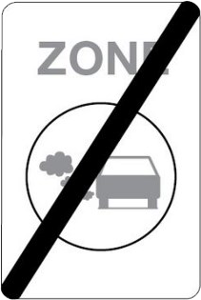 End of the low-emission zone.
End of the low-emission zone.
Left-hand traffic (LHT) and right-hand traffic (RHT) are the practice, in bidirectional traffic, of keeping to the left side or to the right side of the road, respectively. A fundamental element to traffic flow, it is sometimes referred to as the rule of the road.
 In Belgium they drive on the right side of the road, in some countries they drive on the left.
In Belgium they drive on the right side of the road, in some countries they drive on the left.