Main road
If you are driving on a main road, drivers on the side road must give way to you, on the side roads there is a traffic sign with 'give way'. A priority road is a long main road on which you have priority at all following crossroads until the end of the priority road.
- At a main road, road users on the side roads must give way.
- The traffic sign only applies to the next crossroad.
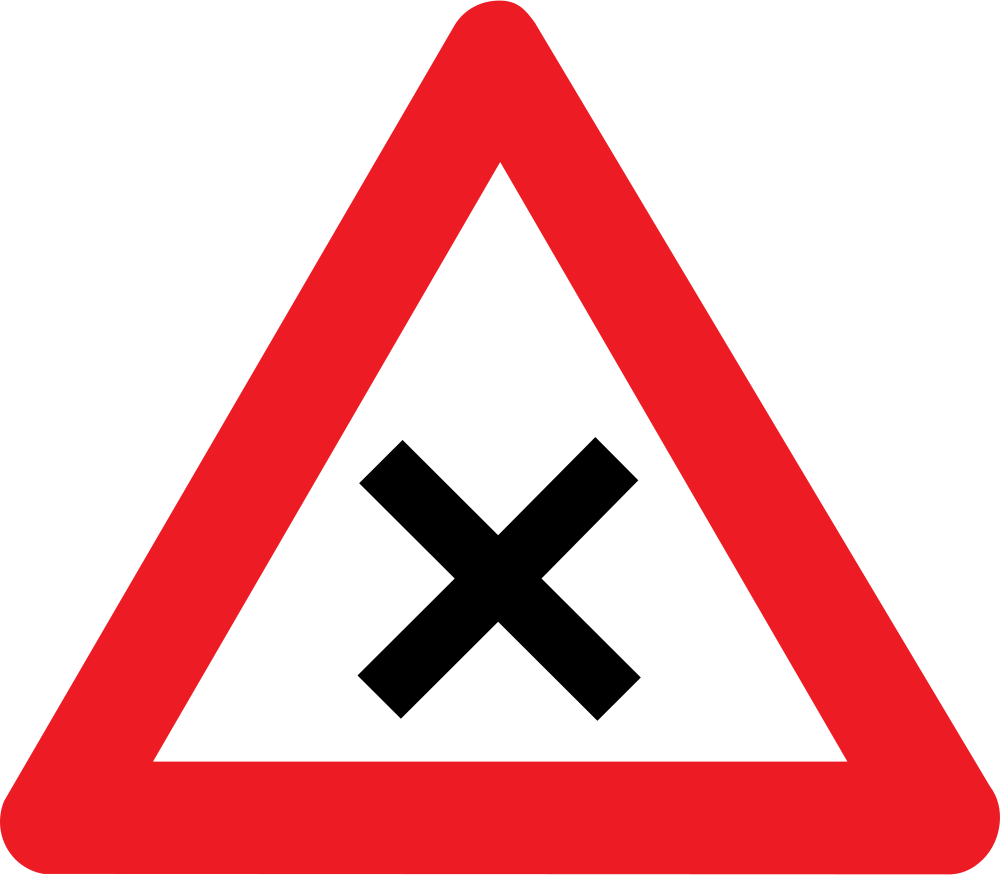
 Warning for a crossroad side roads on the left and right.
Warning for a crossroad side roads on the left and right.
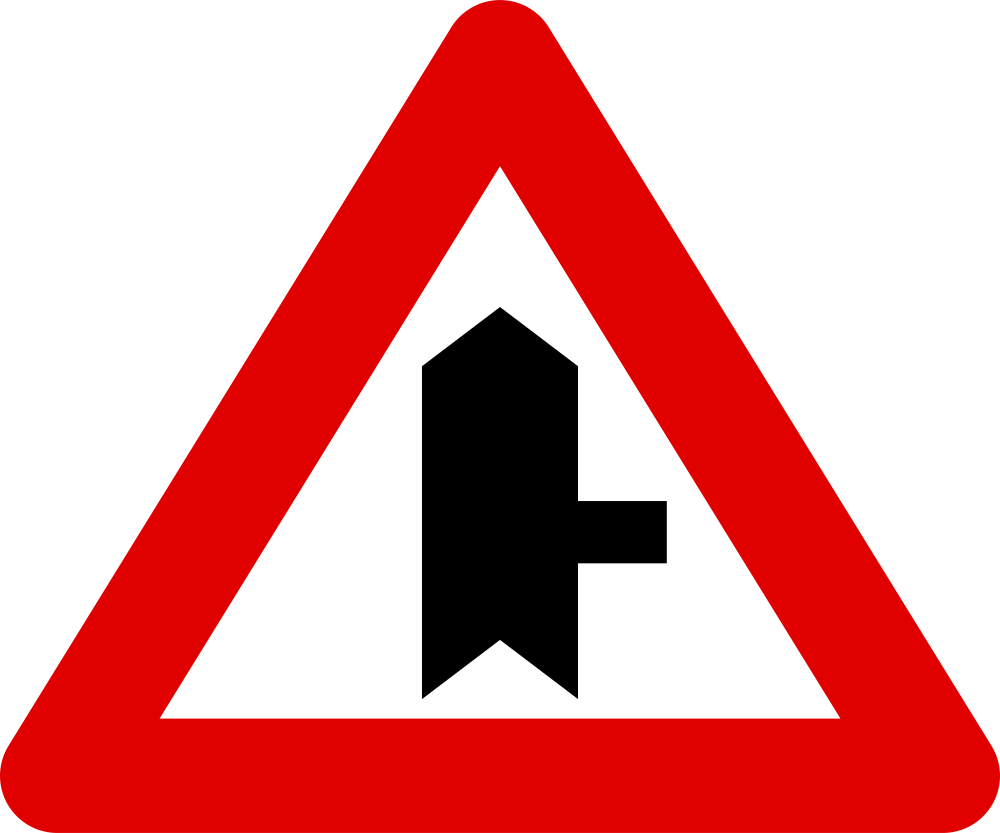 Warning for a crossroad with side road on the right.
Warning for a crossroad with side road on the right.
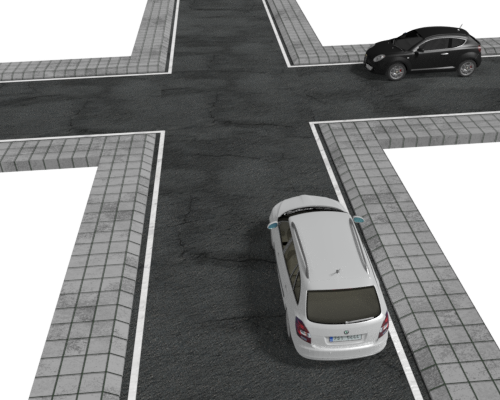

 At an uncontrolled crossroad you must give
At an uncontrolled crossroad you must give 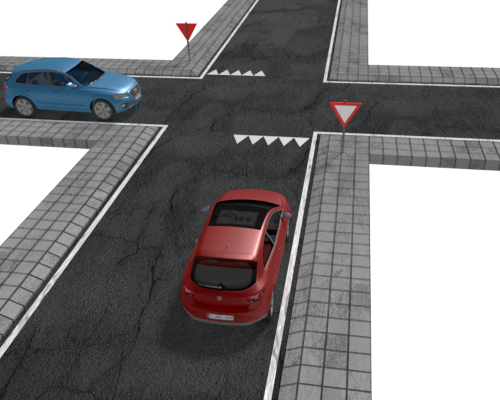 At triangular
At triangular 
 Warning for an
Warning for an 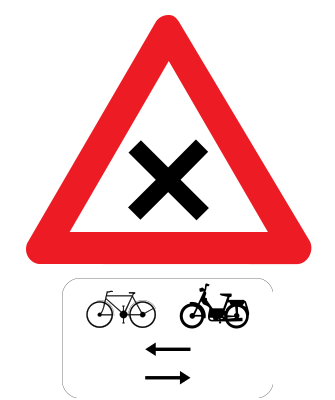 Warning for an
Warning for an 
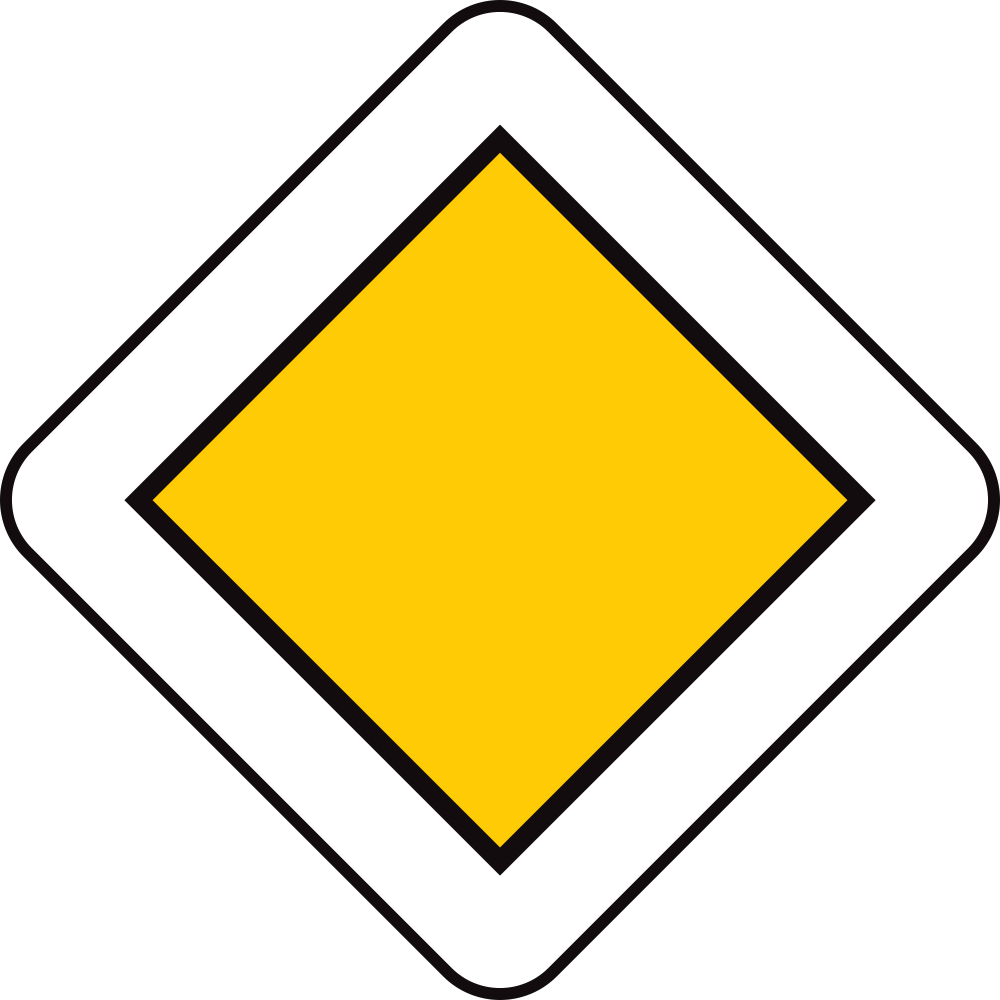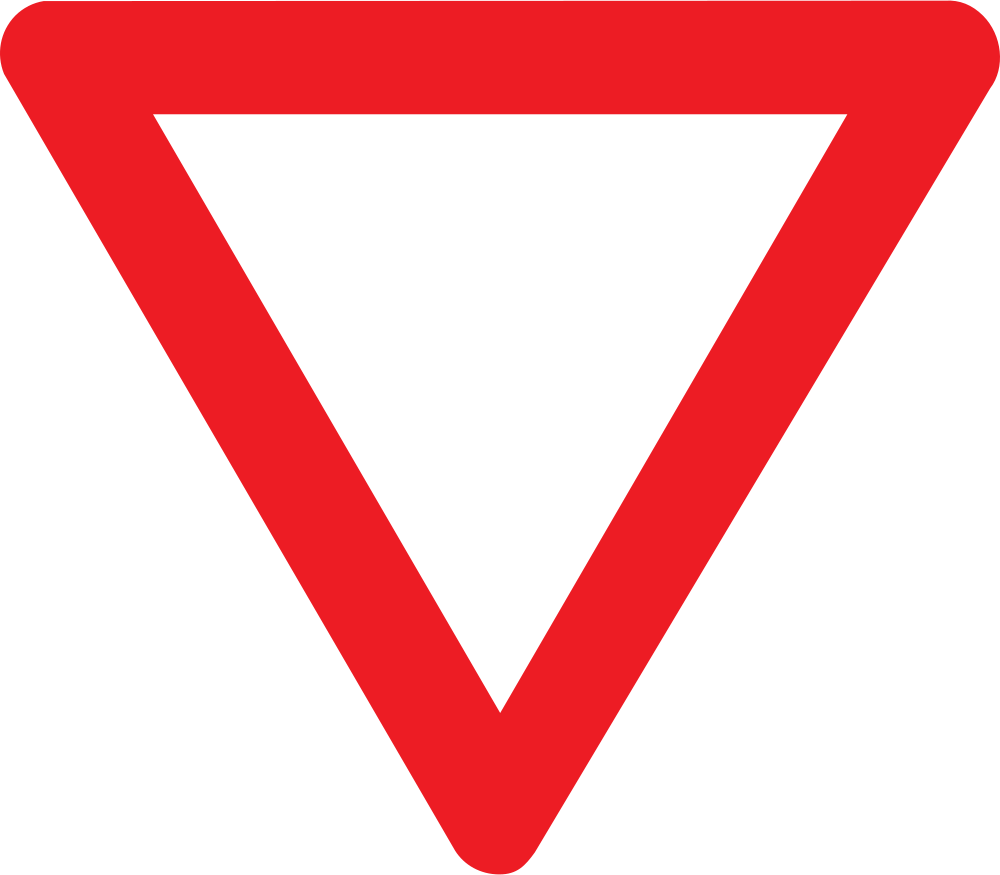

 Begin of a priority road.
Begin of a priority road.
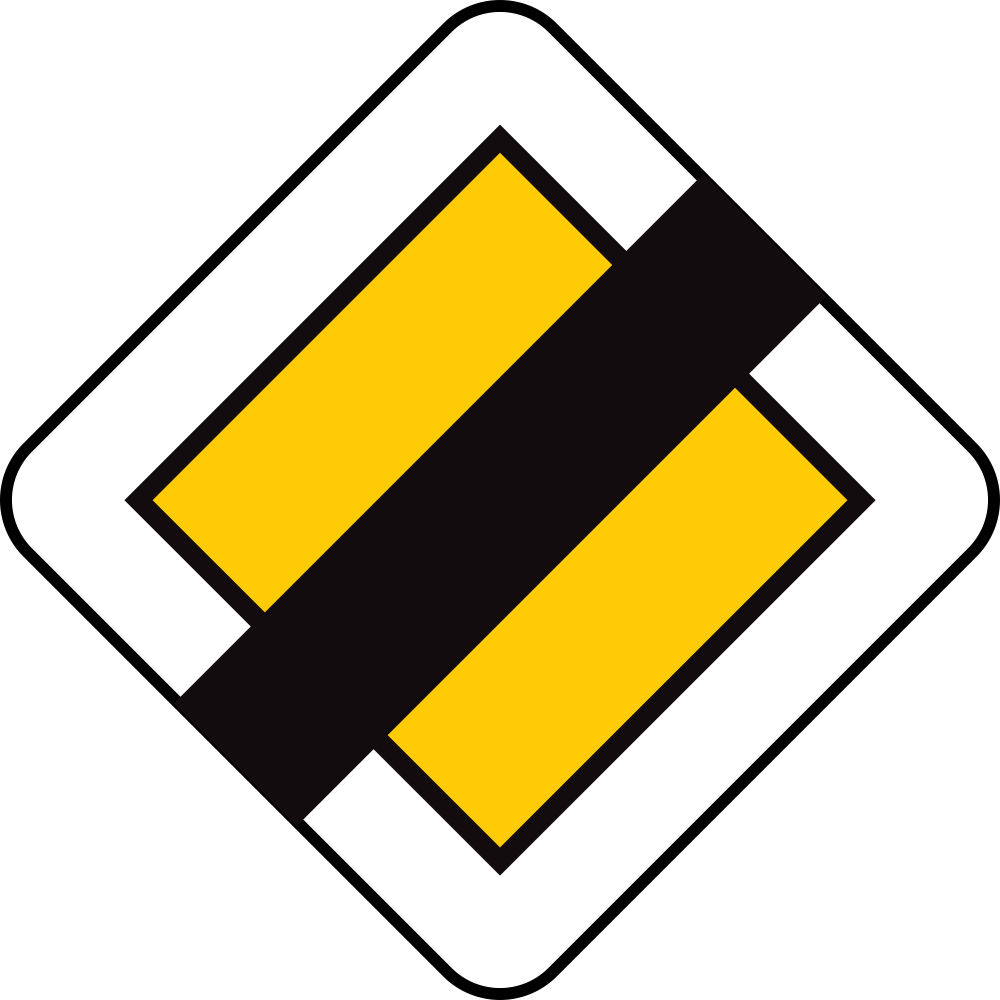 End of the priority road.
End of the priority road.
 Green traffic light
Green traffic light
 Orange traffic light
Orange traffic light
 Red traffic light
Red traffic light
 Green traffic light
Green traffic light
 Red traffic light
Red traffic light
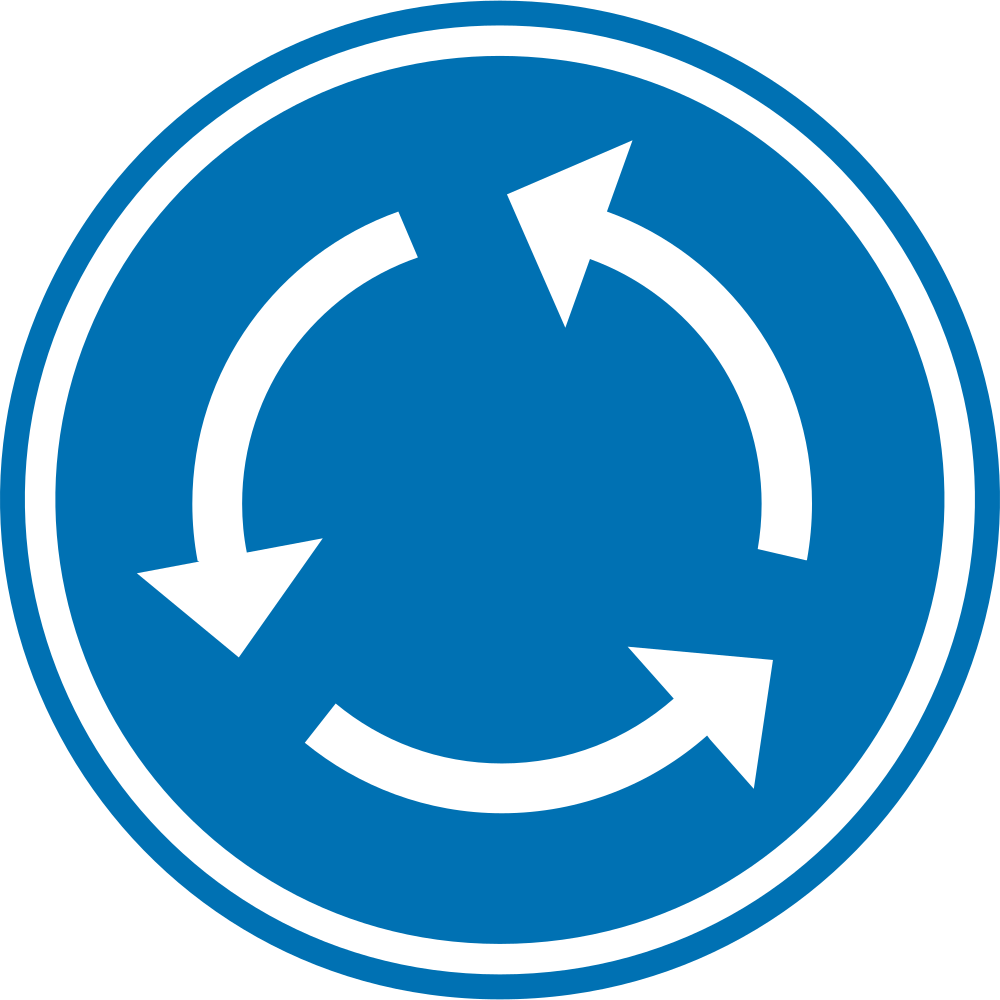 Mandatory direction of the
Mandatory direction of the  In a multi-lane
In a multi-lane 
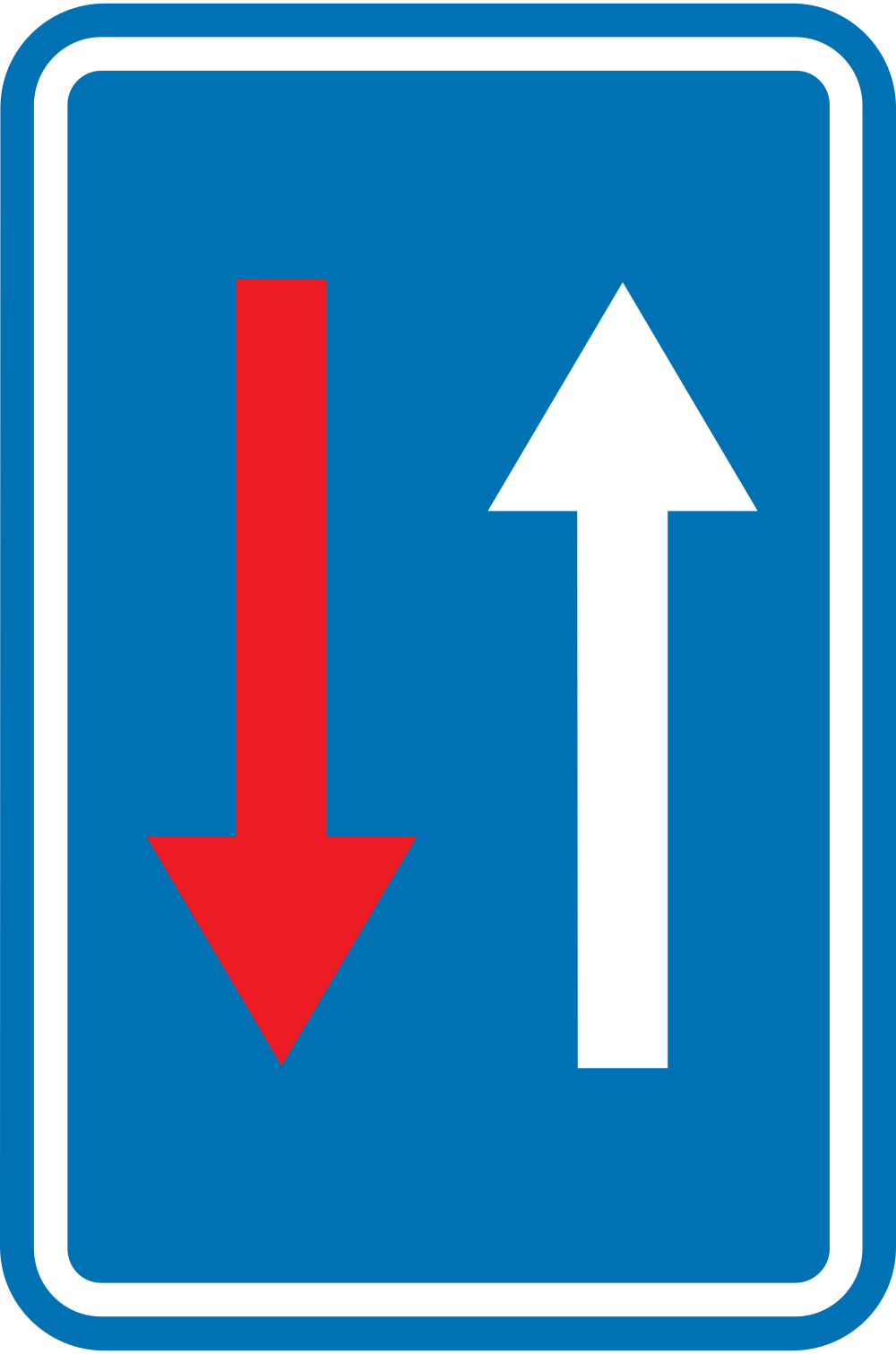 Road narrowing, oncoming drivers have to give way.
Road narrowing, oncoming drivers have to give way.
 Road narrowing, give way to oncoming drivers.
Road narrowing, give way to oncoming drivers.
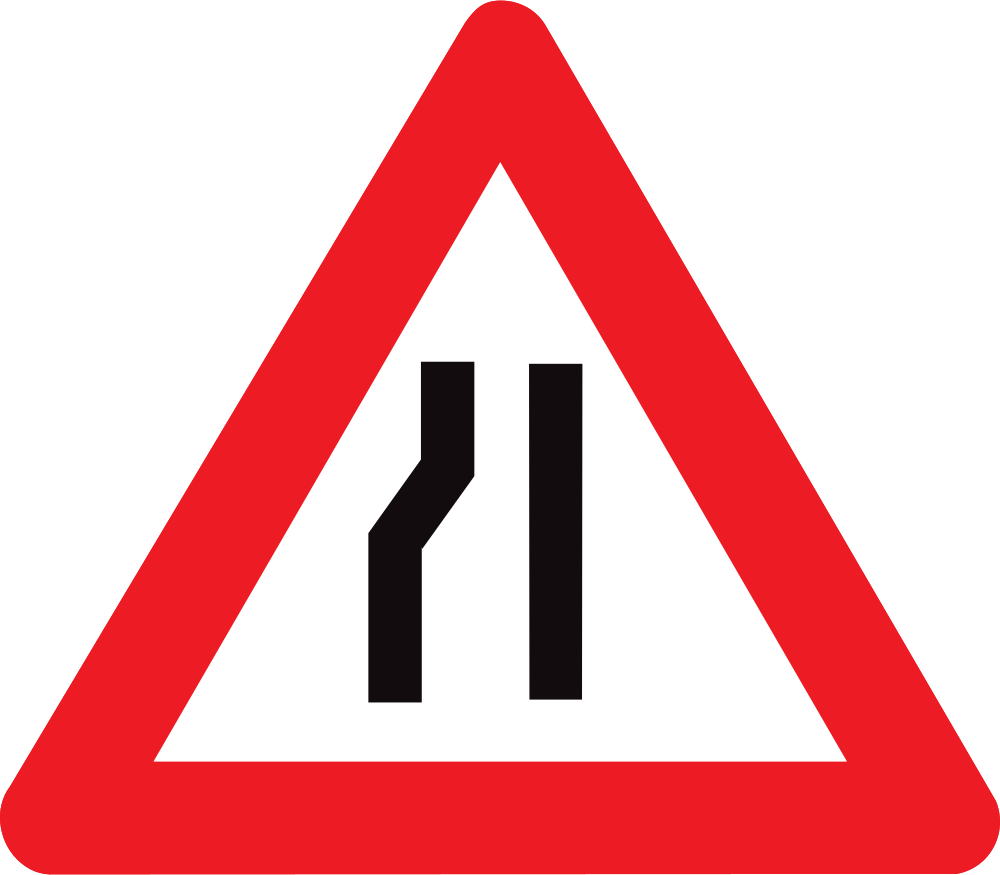 Warning for a road narrowing on the left.
Warning for a road narrowing on the left.
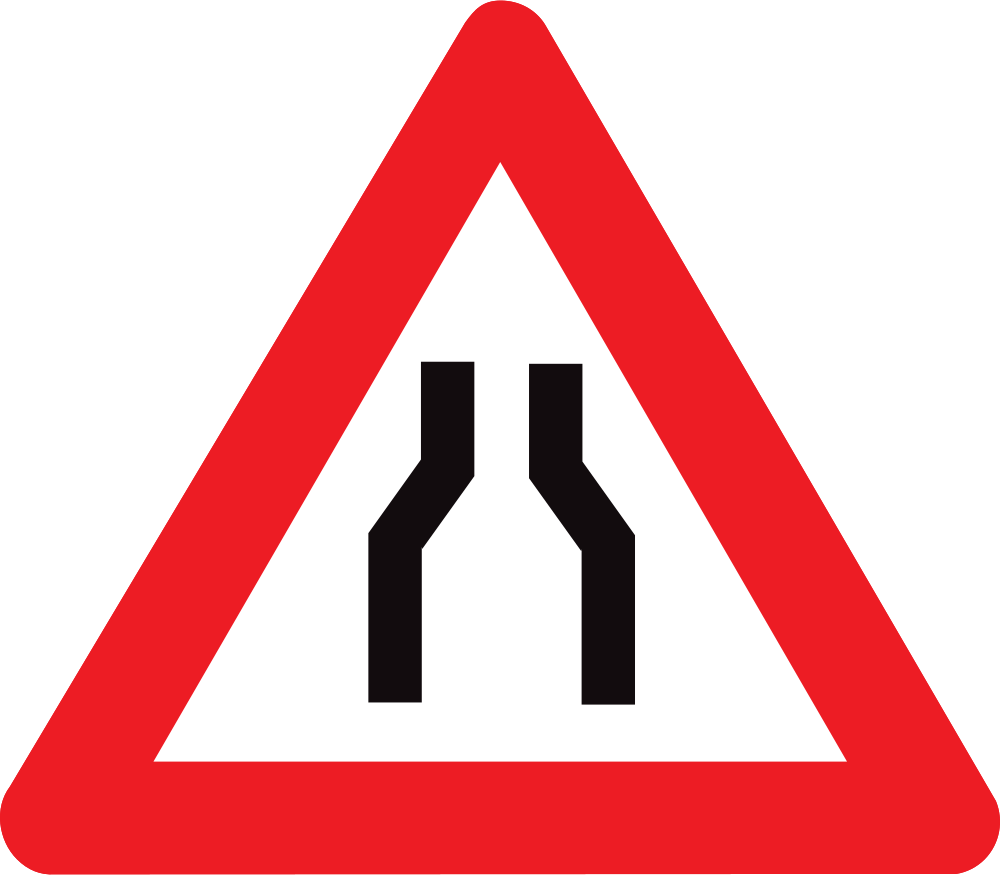 Warning for a road narrowing.
Warning for a road narrowing.
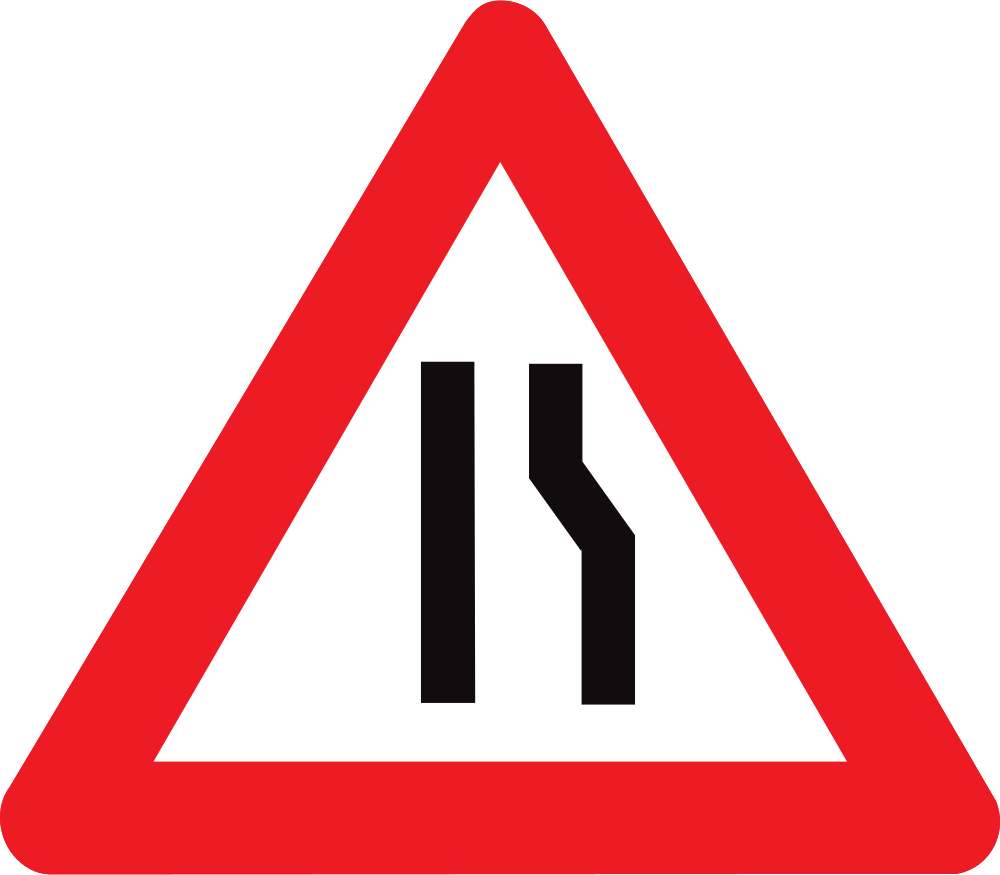 Warning for a road narrowing on the right.
Warning for a road narrowing on the right.

 A
A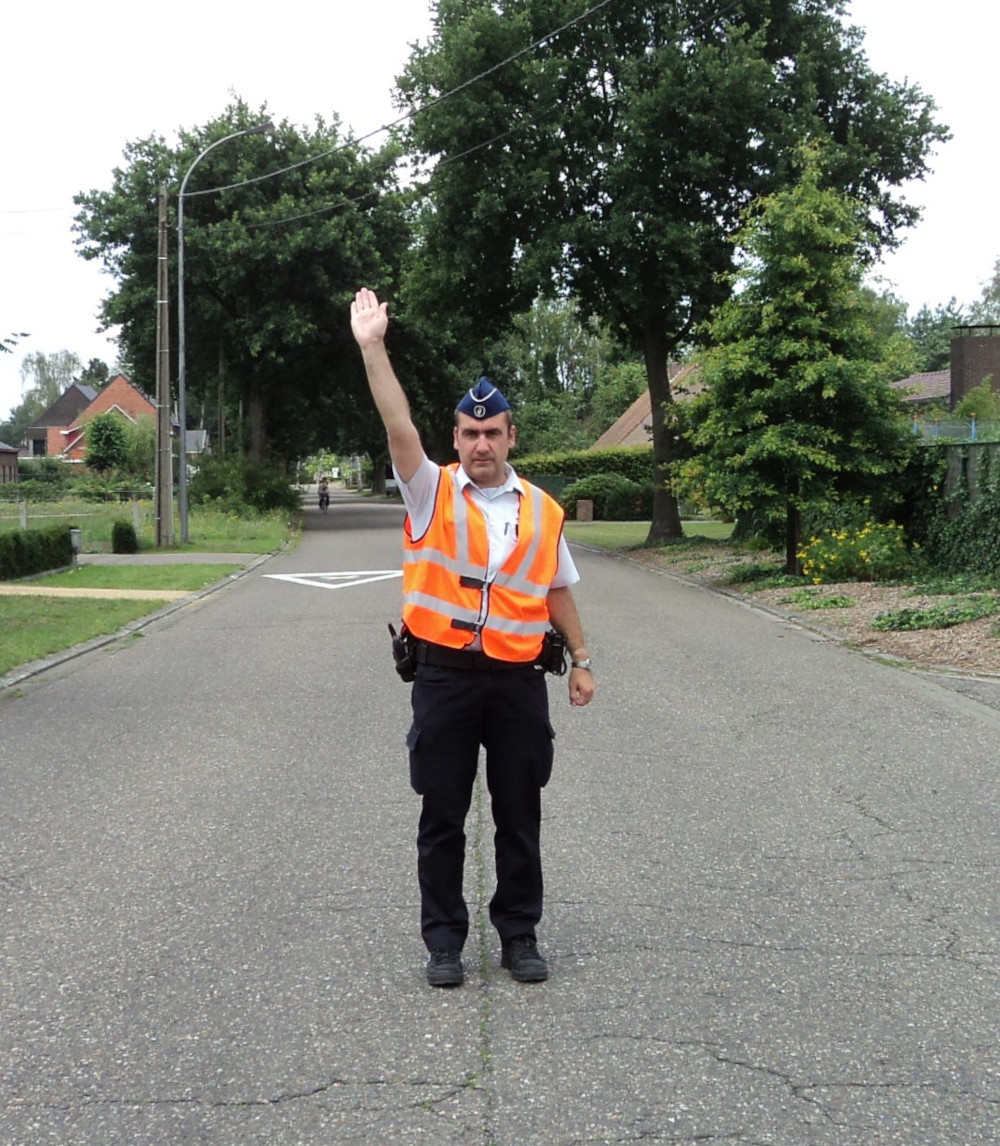  Arm vertical: All road users must stop.
Arm vertical: All road users must stop.
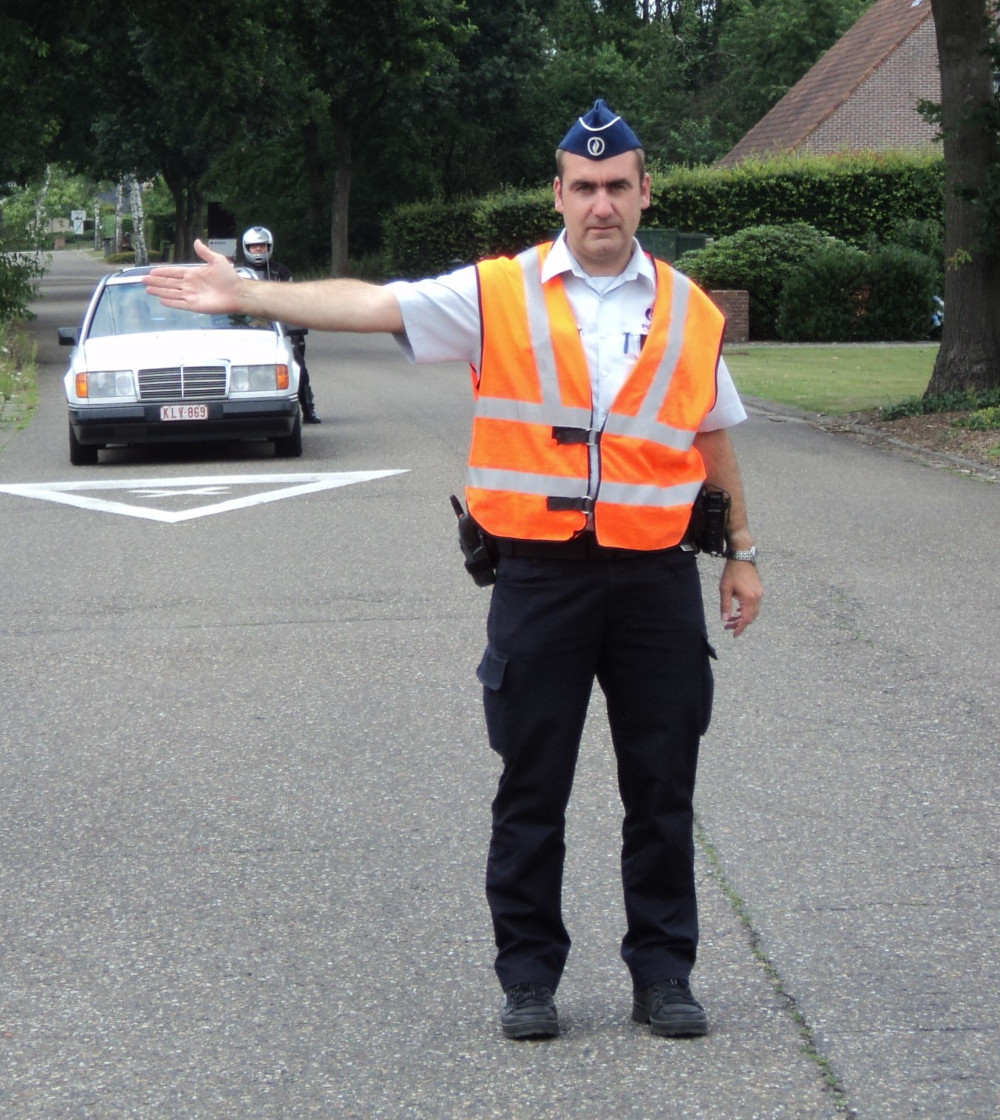 Arm horizontal: Road users who come to his stomach and back stop.
Arm horizontal: Road users who come to his stomach and back stop.
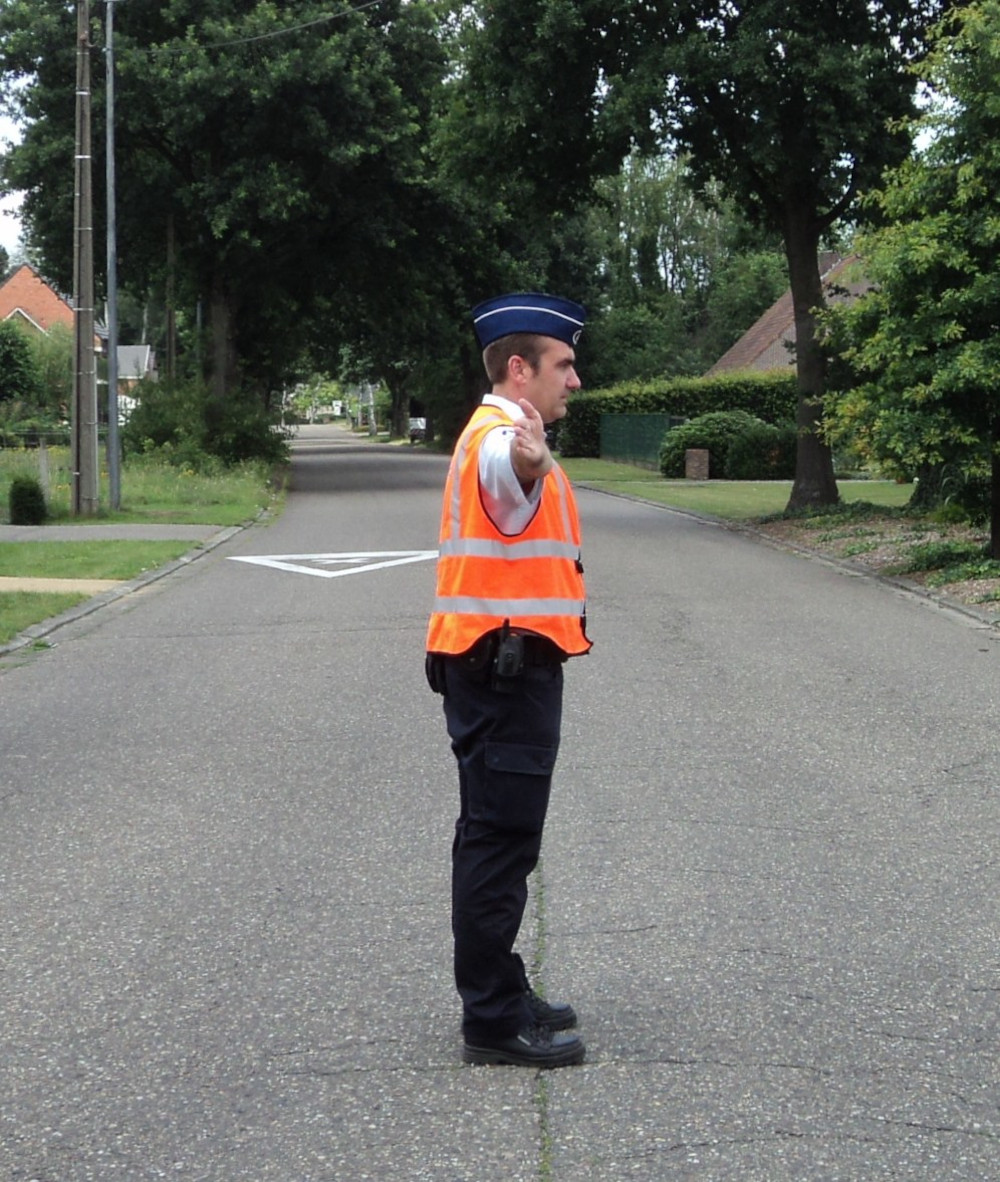 Arm horizontal: Road users approaching their fingertips or side may enter the crossroad.
Arm horizontal: Road users approaching their fingertips or side may enter the crossroad.